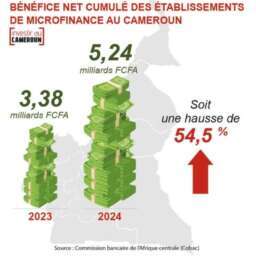
In Cameroon and other developing countries, the evolution from Web 1.0 to Web 3.0 and the emergence of the metaverse hold profound implications for societal development, economic opportunities, and individual empowerment.
1. Access to Information and Knowledge:
The transition from static web pages to interactive, user-generated content in Web 2.0 significantly impacted the way people accessed and shared information. In developing countries like Cameroon, where access to traditional educational resources might be limited, the Internet has played a pivotal role in democratizing knowledge. The potential of Web 3.0 to further enhance decentralized and trustless systems could empower individuals by providing direct access to information without the need for intermediaries.
2. Economic Inclusion and Innovation:
Web 3.0’s focus on decentralized networks and the ownership of personal data can contribute to economic inclusion. In countries with emerging economies, individuals often face challenges related to financial access and ownership. Web 3.0’s emphasis on user ownership and decentralized systems can enable people to participate in the global digital economy on their own terms. This can foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and the creation of digital assets.
3. Addressing Localized Issues:
Decentralized systems in Web 3.0 offer the potential for global villages to address issues that might not have garnered attention on a localized scale. In Cameroon and similar contexts, where communities face unique challenges, the ability to leverage decentralized networks for problem-solving can lead to more inclusive solutions that cater to the population’s specific needs.
4. Preserving Cultural Identity:
The metaverse, with its combination of virtual reality and online spaces, could play a crucial role in preserving and celebrating cultural identity. In countries with rich cultural heritage like Cameroon, the metaverse can provide a digital platform for cultural expression, storytelling, and collaboration. This could be particularly significant in maintaining and transmitting cultural practices to future generations.
5. Digital Skills and Opportunities:
As these technological shifts unfold, early adoption and proficiency with Web 3.0 and the metaverse can empower individuals in developing countries. Gaining expertise in these technologies could open up new avenues for digital skills development, remote work, and participation in the global digital marketplace. Understanding and navigating these emerging landscapes early on can provide a competitive advantage.
6. Challenges and Considerations:
It’s essential to acknowledge that adopting these technologies comes with challenges, including issues related to digital literacy, infrastructure development, and potential disparities in access. Governments, businesses, and educational institutions in developing countries need to be proactive in addressing these challenges to ensure that the benefits of the evolving internet landscape are equitably distributed.
In conclusion, as the internet evolves into Web 3.0 and the metaverse, the implications for developing countries like Cameroon are significant. These technologies have the potential to democratize access, foster economic inclusion, address localized challenges, preserve cultural identity, and create new opportunities. As the digital landscape transforms, proactive engagement, education, and strategic planning will be crucial for these countries to harness the full potential of these technological advancements. Early adopters stand to gain not just in terms of economic opportunities but also in shaping the digital future of their societies.